If you share a vision of educating the public about human origins, our transition to modern life, and behavioral biology, please get in touch ([email protected]).
Human Bridges’s early goals are in recruiting and cohering a group of experts from the fields of human biology, human origins, and anthropology who want to contribute their individual expertise to a wider accessible body of information, and enlist in the cause to make this material a staple of education at all stages of life.
Click here to read the article on Pressenza.
By Jan Ritch-Frel
Discoveries in the fields of human origins, paleoanthropology, cognitive science, and behavioral biology have accelerated in the past few decades. We occasionally bump into news reports that new findings have revolutionary implications for how humanity lives today—but the information for the most part is still packed obscurely in the worlds of science and academia.
Some experts have tried to make the work more accessible, but Deborah Barsky’s new book, Human Prehistory: Exploring the Past to Understand the Future (Cambridge University Press, 2022), is one of the most authoritative yet. The breadth and synthesis of the work are impressive, and Barsky’s highly original analysis on the subject—from the beginnings of culture to how humanity began to be alienated from the natural world—keeps the reader engaged throughout.
Long before Jane Goodall began telling the world we would do well to study our evolutionary origins and genetic cousins, it was a well-established philosophical creed that things go better for humanity the more we try to know ourselves.
Barsky, a researcher at the Catalan Institute of Human Paleoecology and Social Evolution and associate professor at the Open University of Catalonia (UOC) and Rovira i Virgili University in Tarragona, Spain, who came to this field through her decades of studying ancient stone tool technologies, writes early in her book that lessons learned from the remote past could guide our species toward a brighter future, but “that so much of the information that is amassed by prehistoric archeologists remains inaccessible to many people” and “appears far removed from our daily lives.” I reached out to Barsky in the early stage of her book launch to learn more.
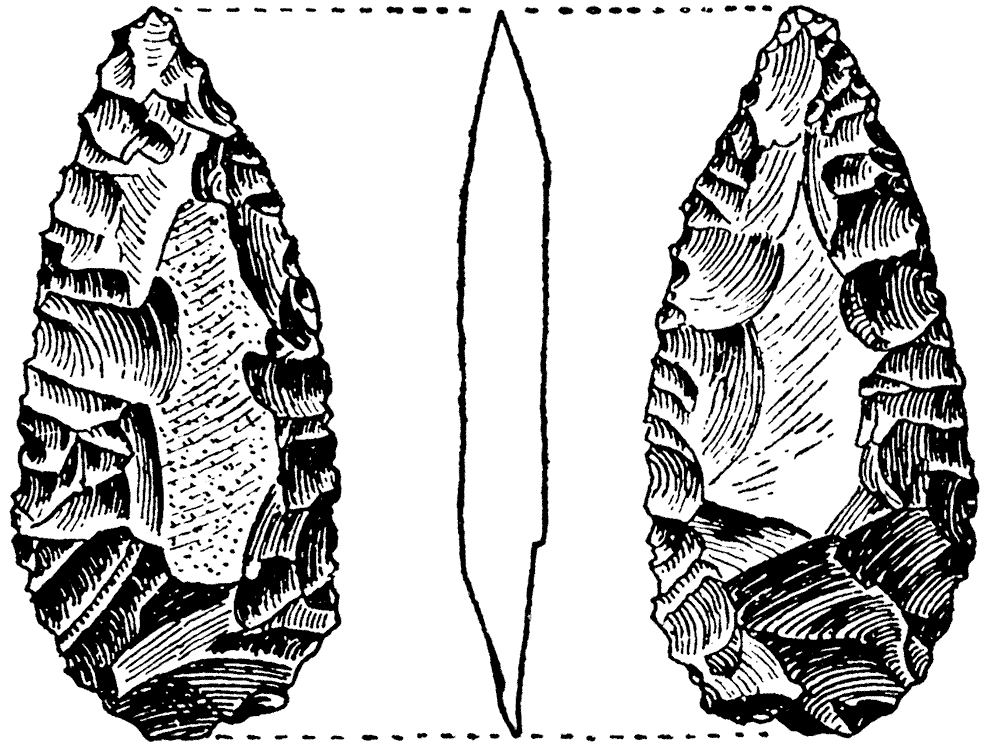
Jan Ritch-Frel: What would you suggest a person consider as they hold a 450,000-year-old handaxe for the first time?
Deborah Barsky: I think everyone feels a deep-seated reverence when touching or holding such an ancient tool. Handaxes in particular carry so many powerful implications, including on the symbolic level. You have to imagine that these tear-shaped tools—the ultimate symbol of the Acheulian—appeared in Africa some 1.75 million years ago and that our ancestors continued creating and re-creating this same shape from that point onwards for more than a million and a half years!
These tools are the first ones recognized as having been made in accordance with a planned mental image. And they have an aesthetic quality, in that they present both bilateral and bifacial symmetry. Some handaxes were made in precious or even visually pleasing rock matrices and were shaped with great care and dexterity according to techniques developed in the longest-enduring cultural norm known to humankind.
And yet, in spite of so many years of studying handaxes, we still understand little about what they were used for, how they were used, and, perhaps most importantly, whether or not they carry with them some kind of symbolic significance that escapes us. There is no doubt that the human capacity to communicate through symbolism has been hugely transformative for our species.
Today we live in a world totally dependent on shared symbolic thought processes, where such constructs as national identity, monetary value, religion, and tradition, for example, have become essential to our survival. Complex educational systems have been created to initiate our children into mastering these constructed realities, integrating them as fully as possible into this system to favor their survival within the masses of our globalized world. In the handaxe we can see the first manifestations of this adaptive choice: to invest in developing symbolic thought. That choice has led us into the digital revolution that contemporary society is now undergoing. Yet, where all of this will lead us remains uncertain.
JRF: Your book shows that it is more helpful to us if we consider the human story and evolution as less of a straight line and more so as one that branches in different ways across time and geography. How can we explain the past to ourselves in a clear and useful way to understand the present?
DB: One of the first things I tell my students is that in the field of human prehistory, one must grow accustomed to information that is in a constant state of flux, as it changes in pace with new discoveries that are being made on nearly a daily basis.
It is also important to recognize that the pieces composing the puzzle of the human story are fragmentary, so that information is constantly changing as we fill in the gaps and ameliorate our capacity to interpret it. Although we favor scientific interpretations in all cases, we cannot escape the fact that our ideas are shaped by our own historical context—a situation that has impeded correct explanations of the archeological record in the past.
One example of this is our knowledge of the human family that has grown exponentially in the last quarter of a century thanks to new discoveries being made throughout the world. Our own genus, Homo, for example, now includes at least five new species, discovered only in this interim.
Meanwhile, genetic studies are taking major steps in advancing the ways we study ancient humans, helping to establish reliable reconstructions of the (now very bushy) family tree, and concretizing the fact that over millions of years multiple hominin species shared the same territories. This situation continued up until the later Paleolithic, when our own species interacted and even reproduced together with other hominins, as in the case of our encounters with the Neandertals in Eurasia, for example.
While there is much conjecture about this situation, we actually know little about the nature of these encounters: whether they were peaceful or violent; whether different hominins transmitted their technological know-how, shared territorial resources together, or decimated one another, perhaps engendering the first warlike behaviors.
One thing is sure: Homo sapiens remains the last representative of this long line of hominin ancestors and now demonstrates unprecedented planetary domination. Is this a Darwinian success story? Or is it a one-way ticket to the sixth extinction event—the first to be caused by humans—as we move into the Anthropocene Epoch?
In my book, I try to communicate this knowledge to readers so that they can better understand how past events have shaped not only our physical beings but also our inner worlds and the symbolic worlds we share with each other. It is only if we can understand when and how these important events took place—actually identify the tendencies and put them into perspective for what they truly are—that we will finally be the masters of our own destiny. Then we will be able to make choices on the levels that really count—not only for ourselves, but also for all life on the planet. Our technologies have undoubtedly alienated us from these realities, and it may be our destiny to continue to pursue life on digital and globalized levels. We can’t undo the present, but we can most certainly use this accumulated knowledge and technological capacity to create far more sustainable and “humane” lifeways.
JRF: How did you come to believe that stone toolmaking was the culprit for how we became alienated from the world we live in?
DB: My PhD research at Perpignan University in France was on the lithic assemblages from the Caune de l’Arago cave site in southern France, a site with numerous Acheulian habitation floors that have been dated to between 690,000 and 90,000 years ago. During the course of my doctoral research, I was given the exceptional opportunity to work on some older African and Eurasian sites. I began to actively collaborate in international and multidisciplinary teamwork (in the field and in the laboratory) and to study some of the oldest stone tool kits known to humankind in different areas of the world. This experience was an important turning point for me that subsequently shaped my career as I oriented my research more and more towards understanding these “first technologies.”
More recently, as a researcher at the Catalan Institute of Human Paleoecology and Social Evolution (IPHES-CERCA) in Tarragona, Spain, I continue to investigate the emergence of ancient human culture, in particular through the study of a number of major archeological sites attributed to the so-called “Oldowan” technocomplex (after the eponymous Olduvai Gorge Bed I sites in Tanzania). My teaching experience at the Open University of Catalonia (UOC) and Rovira i Virgili University (Tarragona) helped me to articulate my findings through discussions and to further my research with students and colleagues.
Such ancient tool kits, some of which date to more than 2 million years ago, were made by the hands of hominins who were very different from ourselves, in a world that was very distinct from our own. They provide a window of opportunity through which to observe some of the cognitive processes employed by the early humans who made and used them. As I expanded my research, I discovered the surprising complexity of ancient stone toolmaking, eventually concluding that it was at the root of a major behavioral bifurcation that would utterly alter the evolutionary pathways taken by humankind.
Early hominins recognizing the advantages provided by toolmaking made the unconscious choice to invest more heavily in it, even as they gained time for more inventiveness. Oldowan tool kits are poorly standardized and contain large pounding implements, alongside small sharp-edged flakes that were certainly useful, among other things, for obtaining viscera and meat resources from animals that were scavenged as hominins competed with other large carnivores present in the paleolandscapes in which they lived. As hominins began to expand their technological know-how, successful resourcing of such protein-rich food was ideal for feeding the developing and energy-expensive brain.
Meanwhile, increased leisure time fueled human inventiveness, and stone tool production—and its associated behaviors—grew ever more complex, eventually requiring relatively heavy investments into teaching these technologies to enable them to pass onwards into each successive generation. This, in turn, established the foundations for the highly beneficial process of cumulative learning that was later coupled with symbolic thought processes such as language that would ultimately favor our capacity for exponential development. This also had huge implications, for example, in terms of the first inklings of what we call “tradition”—ways to make and do things—that are indeed the very building blocks of culture. In addition, neuroscientific experiments undertaken to study the brain synapses involved during toolmaking processes show that at least some basic forms of language were likely needed in order to communicate the technologies required to manufacture the more complex tools of the Acheulian (for example, handaxes).
Moreover, researchers have demonstrated that the areas of the brain activated during toolmaking are the same as those employed during abstract thought processes, including language and volumetric planning. I think that it is clear from this that the Oldowan can be seen as the start of a process that would eventually lead to the massive technosocial database that humanity now embraces and that continues to expand ever further in each successive generation, in a spiral of exponential technological and social creativity.
JRF: Did something indicate to you at the outset of your career that archeology and the study of human origins have a vital message for humanity now? You describe a conceptual process in your book whereby through studying our past, humanity can learn to “build up more viable and durable structural entities and behaviors in harmony with the environment and innocuous to other life forms.”
DB: I think most people who pursue a career in archeology do so because they feel passionate about exploring the human story in a tangible, scientific way. The first step, described in the introductory chapters of my book, is choosing from an ever-widening array of disciplines that contribute to the field today. From the onset, I was fascinated by the emergence and subsequent transformation of early technologies into culture. The first 3 million years of the human archeological record are almost exclusively represented by stone tools. These stone artifacts are complemented by other kinds of tools—especially in the later periods of the Paleolithic, when bone, antler, and ivory artifacts were common—alongside art and relatively clear habitational structures.
It is one thing to analyze a given set of stone tools made by long-extinct hominin cousins and quite another to ask what their transposed significance to contemporary society might be.
As I began to explore these questions more profoundly, numerous concrete applications did finally come to the fore, thus underpinning how data obtained from the prehistoric register is applicable when considering issues such as racism, climate change, and social inequality that plague the modern globalized world.
In my opinion, the invention and subsequent development of technology was the inflection point from which humanity was to diverge towards an alternative pathway from all other life forms on Earth. We now hold the responsibility to wield this power in ways that will be beneficial and sustainable to all life.
Click here to read the article on Pressenza.
Jan Ritch-Frel is the executive director of the Independent Media Institute.